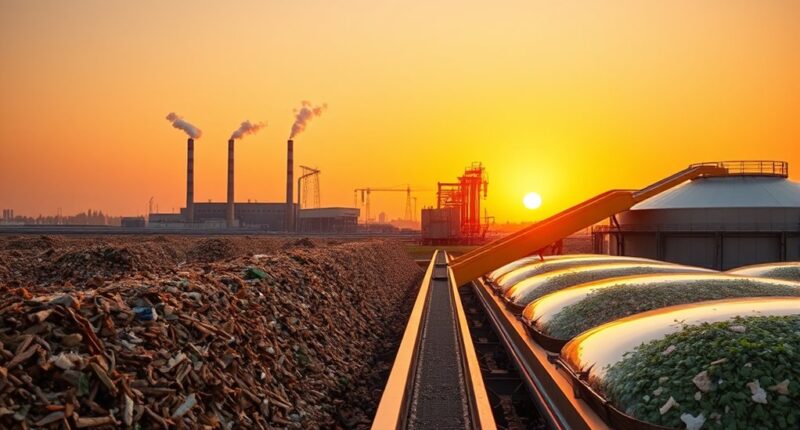
Biomass conversion turns waste materials like crop residues, food scraps, and manure into useful energy sources such as heat, electricity, or biofuels. By recognizing the type of waste, you can choose the most efficient technology—like combustion, gasification, or fermentation—that suits the feedstock’s properties. This process not only reduces waste but also offers a renewable alternative to fossil fuels. Continue exploring to discover how different methods optimize energy production from waste materials.
Key Takeaways
- Biomass conversion transforms organic waste into energy through methods like combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
- Recognizing feedstock type and properties ensures selection of the most efficient and suitable conversion technology.
- Different biomass types require specific processing techniques to optimize energy extraction and environmental benefits.
- Proper technology choice from waste improves renewable energy production and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Utilizing biomass waste for energy supports sustainable waste management and environmental sustainability.
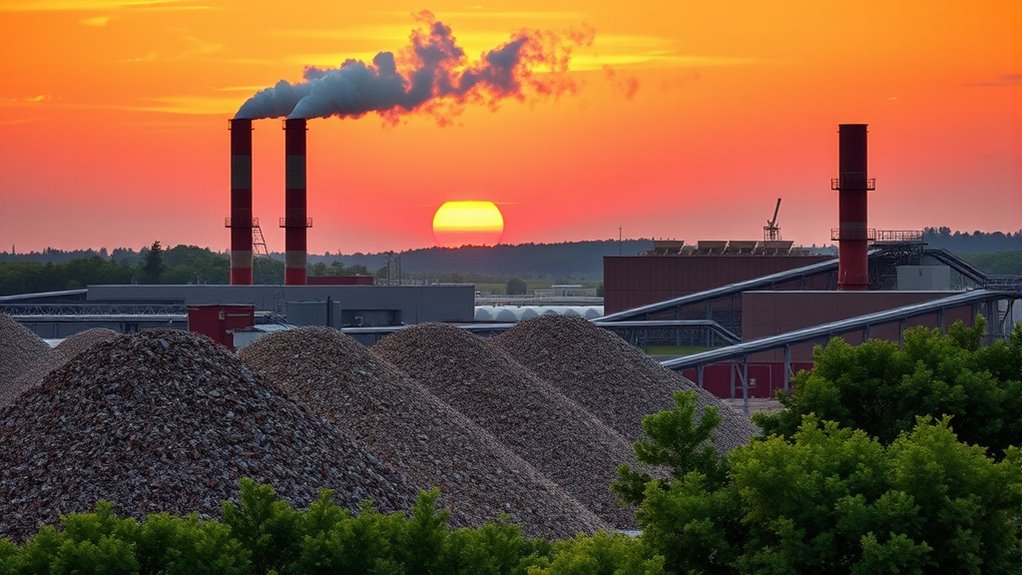

Have you ever wondered how organic materials can be transformed into useful energy? It’s fascinating to realize that the waste we produce daily—like crop residues, forestry leftovers, or food scraps—can serve as a valuable resource for generating power. The key lies in understanding the feedstock variety and the various conversion technologies available. Different types of biomass, whether they’re agricultural waste, animal manure, or even algae, are considered feedstock. Each has unique properties that influence how efficiently it can be converted into energy. For example, lignocellulosic biomass such as wood chips and straw require specific processes due to their complex structure, while liquid feedstocks like food waste can be processed differently. Recognizing this feedstock variety is essential because it determines which conversion technology to use, ensuring ideal energy extraction. Additionally, the composition of biomass impacts the choice of conversion method and overall efficiency.
Conversion technologies are the methods that transform these raw materials into usable energy forms, such as heat, electricity, or biofuels. One common approach is direct combustion, where biomass is burned to produce heat, which then drives turbines to generate electricity. This method is straightforward and has been used for centuries, but it’s not always the most efficient or environmentally friendly option. More advanced techniques include gasification, where biomass is heated in a low-oxygen environment to produce syngas. This versatile gas can be used to generate electricity, produce chemicals, or be converted into transportation fuels. Another important technology is anaerobic digestion, which involves breaking down organic waste in oxygen-free conditions, resulting in biogas—mainly methane—that can be used for heating, electricity, or as a vehicle fuel. Fermentation processes also play a role, especially in producing bioethanol from crops like corn or sugarcane.
Choosing the right conversion technology depends heavily on the feedstock type and the desired energy output. For instance, if you’re dealing with high-moisture waste, anaerobic digestion might be your best option because it handles wet organic material efficiently. Conversely, for dry woody biomass, gasification or combustion could be more suitable. By understanding the feedstock variety and selecting appropriate conversion technologies, you can maximize energy recovery and reduce waste. This approach not only offers a sustainable way to handle organic waste but also helps decrease reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to a cleaner environment. In your efforts to turn waste into energy, recognizing these fundamental differences and applying the right technology can make all the difference, transforming what would be discarded into a valuable, renewable resource.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Biomass Conversion?
You should consider that biomass conversion can reduce waste and lower greenhouse gases, but it might also cause air pollution through emissions like particulate matter and carbon monoxide. Additionally, land use changes are necessary for growing feedstocks, which could impact local ecosystems and biodiversity. While this process offers renewable energy benefits, you need to make sure these environmental impacts carefully to ensure sustainable practices.
How Cost-Effective Is Biomass Energy Compared to Fossil Fuels?
Biomass energy is generally more cost-effective than fossil fuels because it offers better economic viability and enhances market competitiveness. You’ll find that biomass often has lower fuel costs, reduces dependence on imported fuels, and benefits from government incentives. While initial setup may be higher, ongoing expenses tend to be lower, making biomass a more financially sustainable choice. Overall, it’s a smart, affordable option that’s gaining traction in the energy market.
What Types of Waste Are Most Suitable for Biomass Conversion?
You can mainly use organic residues and agricultural waste for biomass conversion, as they’re abundant and easily available. Organic residues like food scraps, forestry byproducts, and crop leftovers are ideal because they have high energy content. Agricultural waste, including straw, husks, and stalks, also works well since it’s often discarded or burned, causing pollution. Using these waste types helps you produce renewable energy while reducing environmental harm.
Are There Any Health Risks Associated With Biomass Energy Production?
Like Pandora’s box, biomass energy production can pose health concerns if not managed properly. You might face risks from air pollution, including particulate matter and harmful gases released during combustion. These emissions can cause respiratory issues and other health problems. To minimize these risks, make certain proper filtration and emission controls are in place, and stay informed about local regulations to protect yourself and your community from potential hazards.
How Scalable Are Biomass Conversion Technologies for Global Use?
You can see that biomass conversion technologies face significant scalability challenges, which affect their global adoption. As you consider expanding these systems worldwide, you’ll encounter issues like resource availability, infrastructure development, and cost. While these technologies hold promise for sustainable energy, overcoming scalability challenges is vital to guarantee they can be widely adopted and effectively contribute to global energy needs.
Conclusion
By harnessing biomass conversion, you hold the power to turn waste into a nearly limitless energy source, transforming trash into a renewable resource that could save our planet. Every piece of waste you repurpose fuels a cleaner, greener future—more essential than ever before. This isn’t just about energy; it’s about rewriting the story of waste and sustainability. Embrace this revolution, because the impact you make could be as monumental as rewriting history itself.